As an Android user, you will one day come across a term that is unfamiliar in the system. The term root or ROM is one of those terms that you may not be familiar with. It’s not just English words. Or a term whose meaning you will learn later. Each term can branch into several other terms. And each branch branches off into the other, Android is a simple system when it comes to dealing with it, but its complexity is that you know it and you know everything about it. Therefore, this topic is for your reference. Learn the most important Android terms. Only from a purely technical point of view.
The most important basic Android terms
* Root
* Rom
* Kernel
* Recovery
Top Android sub terms
* Bootloader
* Stock Rom
* Custom Rom
Root

In translation, this means the root of the plant. The roots are responsible for providing all the food and water the plant needs from the soil. Since Android is based on Linux, it shares the same terminology as it does. Being a Linux means root extension /0, the initial system file that provides everything for the system. Any modification to it may damage your device. But the difference is that a common destination for rooting on Android is a set of privileges and permissions that a user acquires in order to be able to modify the system of their Android device. These permissions can be obtained through one of the two applications, Magisk or SuperSu, which we discuss later in this topic. But the most important thing you need about root is that you need an unlocked bootloader, which brings us to the first subkey.
Bootloader

Unofficial system changes can harm the phone, hence the role of the bootloader. Before we get into the definitions, remember that changes don’t harm hardware, but bad changes do. As if I am playing a file from another device on my personal computer without calculating the result of this command. The system firewall from modifying the boot loader. Since the device can be modified in any way, the bootloader must be unlocked first. It is a valid method because you need to have the company’s permission to unlock the bootloader. Whether you use a special code to unlock, as in previous Sony devices. Or through the Mi account statement of Xiaomi phones. It turns out that the bootloader issue is minor and can be easily unlocked. Because there is a rule in programming that all code has holes. you are right. But it’s not that easy. For example, there is Huawei, which completely eliminated the bootloader unlocking. Nobody knows how to decipher it. It’s also possible that your chin is causing problems with your device. Just like Sony did with the Sony Xperia Z3. Because the company loaded the bootloader with camera files and camera drivers. If the bootloader is removed, the camera will be completely broken. All this to prevent unofficial modification of the device. Unofficial modifications may cause issues that are not covered by the hardware warranty.
The most important uses of Root

Some heavy terms. It’s not a difficult term, but there is a lot of debate about it. But let’s start with the basic terms. ROM is whatever your eyes see on your phone, from the moment you turn it on, right down to each color. and exercise. And the shapes that your eyes see. ROM is the system that you use on your device. By type of manufacturer. Let’s agree that ROM starts with Google in its initial form. You’ll find the same consistent, unified look you see on Google Pixel devices. This is the beginning of the ROM. Then the manufacturers started modifying it to make it what you see it. There is Samsung and its interface TouchWiz or the new name Samsung Experience. Samsung’s own ROM also uses the same name. Huawei’s interface is called EMUI, and Xiaomi’s interface is called MIUI. The good thing about Xiaomi is that the company started with the MIUI interface as a kind of custom ROM, and we’ll talk about custom ROM later. The interface name is the name of the company’s ROM. ROM is divided into two types. ROM or custom ROM. So what are they?
Stock ROM
It is the official ROM of the company that comes with the phone. ROM in this case is the best category especially for phones. Because it has been programmed perfectly according to the specifications of the phone. But that doesn’t mean it’s the best option, just leave that up to Custom ROM. But Stock ROM keeps your phone in the most stable state possible for your phone. You get full access to all the manufacturer’s features and benefits. It is ideal for those who want their phone to be stable and not need to monitor it much afterwards.
Custom ROM
Developers independent of the company are diligent. One of the developers who owns the phone is building a custom ROM for the phone. Either by modifying the stock ROM or building another ROM from scratch. Custom ROMs have other advantages over stock ROMs. It can, but it depends on the possibility of better performance on the custom ROM. But it’s up to the developer and their modifications. Whether it’s called disk or through another custom kernel is a term we’ll discuss later. and custom ROM types. Built naturally on the corporate front. There are also those that are built on the original interface, the most famous of which is Lineage OS. It is the nucleus upon which the rest of the species is built. The remaining types are as follows:
* Pixel Experience
* AOSP Extended
* AOSP
* Havoc OS
* Tipsy OS
* Liquid Remix
* Resurrection Remix
* Carbon OS
* Panaroid ROM
Kernel
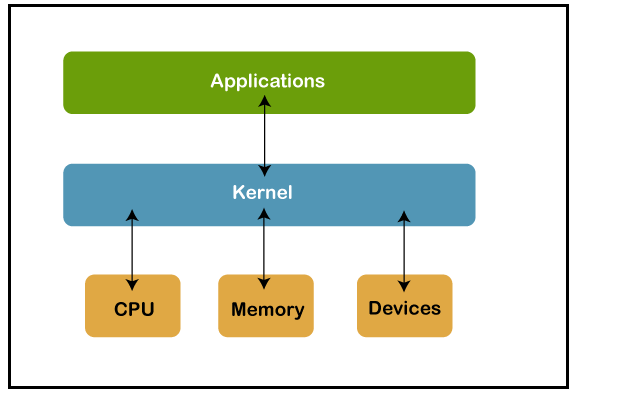
Kernel is a somewhat new term. Your phone consists of two main units. The hardware is the physical pieces that you can hold in your hand. which you can see with your own eyes. The software is what you see on the screen and what you deal with on the phone. And the kernel between them connects the software and the hardware. It is the main link between the two parts. Through it, you can adjust the processor speed, for example. Add systems to save battery power. Control when RAM is dumped. And developers are trying to modify it permanently to get the best possible performance from the phone through modification.
Recovery
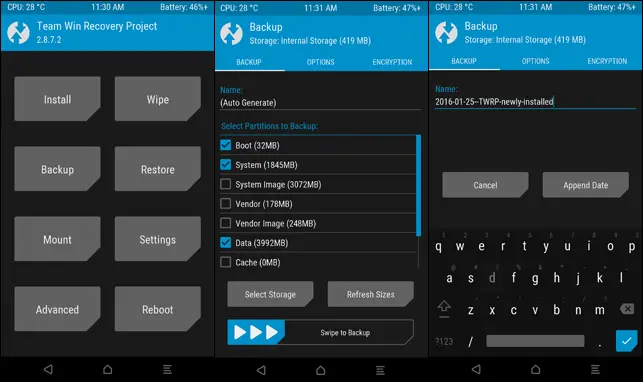
A very important term. Recovery is a software modification mode. Where you can do a lot of things that you may need. For example, if you do a factory reset for a phone. Or just clear the internal memory data. You can also erase the files of the system itself or change the ROM permanently. Recovery is the modification-only mode. And there are two main types. Stock and rate. The Stock Recovery is the company’s with which you can do simple things like doing a factory reset or automatically installing updates. As for the rate, the developers are working on it. Which enables them to do any different modifications, the most famous of which is twrp.





